Alsco’s fully managed First Aid Kit contains perfectly organised treatment supplies for each injury. With regular maintenance and updates, this helps keep your business WH&S compliant and saves you a lot of time and money.
In order to administer proper first aid medication and treatment, we’ll need to understand the terms and terminologies used. There are terms that might be confusing if you’re new to it. The terms and description in this First Aid Glossary will help you understand common first aid concepts and products so you can properly use these whenever the need arises.
Disclaimer: Alsco has endeavoured to ensure that the content of this page is as accurate as possible however no responsibility is accepted for either accurateness or completeness of the material. Alsco reserves the right to make change to First Aid Kit contents as it deems appropriate.
First Aid Medical Terms
Abrasion:
– A medical term used to refer to the damage to the skin through to scraping or wearing away.
Acetaminophen:
– An analgesic pain reliever that is used to reduce fever as well as treat arthritis, headaches and minor pain.
Adrenaline:
– A hormone that increases the heart rate, pulse rate, blood pressure and cause blood vessels to constrict and strengthen in response to stress. A surge of strength and energy brought by a stressful event or dangerous situation is referred as an adrenaline rush.
Airbag:
– A safety device in a vehicle that inflates rapidly when there’s an automobile collision to protect the occupant from striking into objects that may cause injuries.
Airway:
– The respiratory tract where air passes in and out of the lungs. The nose and the mouth are the normal entry and exit ports of the airway.
Anaphylaxis:
– An acute or serious allergic reaction to a chemical or an allergen, potentially life-threatening. For possible serious allergic reaction/anaphylaxis cases, make sure Anaphylaxis First Aid is administered.
Anaesthetic:
– A substance that causes a person to be insensitive to pain or lack of feeling/awareness to pain especially during surgery and other painful procedures.
Angina:
– A medical term that refers to the chest pain or discomfort that is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
Antibiotics:
– Drugs or medicines that are used to treat or prevent bacterial infections. This is also known as antibacterials. Note: Antibiotics have no effect on viral infections.
Artery:
-A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to all parts of the body; contains oxygenated blood. Arteries are part of the circulatory system and is responsible for the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to all cells.
Aspirin:
– A drug that is used to treat mild or moderate pain. It is also used to reduce risks of heart attacks and strokes by preventing blood clots from forming.
Asthma:
– A lung condition that causes difficulty in breathing due to constrictions of the small air tubes in the lungs. It is usually triggered by allergic reaction or other hypersensitivity. There is First Aid for Asthma Attacks that can be practised to provide immediate care.
Automated External Defibrillator:
– A device that restores the normal rhythm of the heart by delivering a controlled electrical shock. A sudden cardiac arrest can happen anytime so AEDs installed in workplaces are necessary as it is an opportunity for life-saving defibrillation.
Avulsion:
– Soft tissue injury; a tearing away of a section of skin or other soft tissue from the deeper layers causing severe bleeding.
Basic Life Support (BLS):
– This is a level of medical care for victims of life-threatening injuries until a full medical care is given to them at the hospital. It can be provided by a BLS trained person, a paramedic or emergency medical technician.
Blood pressure:
– The pressure of the blood within the arteries. This is one of the vital signs being monitored to indicate wellness of the body. It varies depending on activities, situation and stress. Too low or too high levels of blood pressure is not a good sign and will require further medical care. Normal blood pressure in an adult is approximately 120/80 mm Hg.
Blood sugar:
– Also known as blood glucose. Abnormalities in blood sugar levels can either be high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
Breathing:
– The process of which air is inhaled through the mouth or nose, and then air is expelled from the lungs due to muscle contraction and relaxation, respectively.
Bruise:
– An injury caused by an impact that damages soft tissues and underlying blood vessels. Discoloration appears on the area of the body affected; another term for contusion. When you get bruises, check First Aid for Bruises to help you take care and patch them up.
Burn:
– An injury that gives a feeling of discomfort caused by exposure to heat, flame, chemical agents, radiation, or electricity.In case you get caught or find the need to help another person who had burns, check First Aid for Burns.
Calamine:
– An astringent made from zinc oxide or zinc carbonate, usually the main ingredient in anti-pruritic lotion to treat rashes, poison ivy, insect bites, stings or sunburns.
Carbon monoxide poisoning:
– A potentially life-threatening condition caused by inhalation of too much carbon monoxide gas that it prevents oxygenation of the blood. Carbon monoxide is emitted by automobile and engines which should not be run in unventilated spaces.
Cardiac:
– Cardiac is the medical term which means relating to the heart. A sudden stop in effective blood circulation due to the failure of the heart to contract is called a cardiac arrest. An immediate CPR and an AED can help restore the functioning of the heart.
Cardiopulmonary:
– A medical term referring to or relating to the heart and the lungs.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR):
– (AKA: Chest Compressions)/Rescue Breathing (AKA: Artificial Respiration) Also abbreviated as CPR. A life-saving first aid procedure of chest compressions given to patients who is in cardiac arrest. This medical process helps patient’s body pump blood when the heart fails. To carry out this procedure, a trained person manually presses up and down the casualty’s chest (chest compressions) and performs a series of rescue breaths by means of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation which help restore breathing and circulation.
Chest Pain:
– A feeling of tightness, heavy pressure, or crushing pain around the chest area – between the neck and upper abdomen. It can be a result of angina, heart attack, and other important diseases. Chest pain is a warning to seek medical attention.
Choking:
– It is the inability to breathe because the trachea is blocked, constricted, or obstructed. This is caused also by lack of air. It is a common cause of an accident to young children that may lead to death.
Collision:
– Collision is an event when two or more moving bodies collide through an exertion of very strong forces. The term often relates to vehicular accidents.
C-Spine:
– The Cervical spine is the medical term for the neck bones.
Compression:
– Also known as cerebral compression which is usually caused by a head injury. It occurs when there is a build-up of pressure on the brain. Head injuries may lead to permanent mental impairment, disability or even death. Head injury cases require immediate medical attention. First aid for head injury should be administered to prevent further damage to the brain.
Concussion:
– A brain injury that is caused by a sudden blow to the head that shades the brain inside the skull. It can result to confusion, loss of memory with/without headache. First aid for head injury should be administered to prevent further damage to the brain.
Contusion:
– The medical term for bruise. It is caused by injury to the skin tissues or broken blood vessels that usually results in bleeding beneath the skin.
Cuts:
– Cuts or laceration is a wound caused by a tear or a deep cut in the flesh or skin. It can be minor or major depending on the different types of cut and its severity.
Cyanosis:
– Refers to the bluish discoloration near the surface of the skin usually to the hands and feet. This occurs when there’s low oxygen level in red blood cells.
Decongestant:
– A medicine or drug used to relieve nasal congestion and stuffed nose caused by a cold, flu, allergies or sinusitis.
Defibrillator:
– A device that uses electrical shocks to restore normal heartbeat and correct abnormal heart rhythm.
Diabetes:
– Diabetes is a disease in which the blood glucose or blood sugar is abnormally high. A diabetic person can have diabetic attacks which will require medical help.
Diarrhoea:
– Also spelled as Diarrhea. A condition or illness symptomised by having loose or liquid bowel movement of atleast three times each day and can last for several days. It is a symptom or effect of food poisoning, bacterial or viral infection, medication and other underlying causes. What to do when having a diarrhoea? Here are some effective first aid treatment for diarrhoea that you can follow to ease the symptoms.
Dislocation:
– Also known as luxation. This happens when there’s an undesirable separation in the joint at the end of the bone; usually moved out of its normal connection with another bone. Dislocation is usually caused by sudden impact or fall.
Emergency:
– A serious or dangerous situation that requires immediate or urgent action to avoid worsening of the scenario. A situation is considered to be an emergency if it poses an immediate threat to life, property, health or the environment.
Emergency Code:
– Codes used by hospitals to quickly alert staff to different emergencies and relay essential information without causing stress and panic among visitors and patients in the hospital.
Emergency Department:
– Also known as ED or ER (emergency room). It is a medical treatment facility that accommodates emergency cases and provide medical care to patients without prior appointments.
Emergency Oxygen:
– A portable oxygen unit, available in different sized cylinders, that increases a person’s oxygen level internally during emergency cases.
Entonox:
– A medical analgesic gas, often called gas and air. It acts as a safe pain reliever when inhaled and is usually given by ambulance crews.
Epilepsy:
– A neurological condition/disorder characterized by repeated seizures or epileptic attacks. It can be controlled through medication. Epileptic attacks happen when the normal function of the brain is disturbed because of electrical discharge occurence in the brain. First aid for epileptic attacks can be done to avoid injuries and complications.
Ergonomics:
– The science of designing the workplace, job or equipment to fit the worker. It is necessary to prevent strain injuries and long-term disabilities.
Fainting:
– It occurs when there’s a little amount of oxygen supply to the brain, a person loses its consciousness for a short period of time.
Febrile convulsion:
– A seizure that occus in children associated with very high temperature causing the child to overheat.
Fracture:
– A medical term for a broken bone. Bone fractures usually require immediate hospital care. Extra care is needed, do first aid for fractures while you wait for help (ambulance) to arrive.
Frostbite:
– A feeling of numbness or freezing of the skin or other tissues due to extremely low temperatures. Skin turns pale at the start then turns red and cold.
Glucose:
– A medical term for simple sugar found in blood that is the main source of energy in the body.
Health Care Professional: (AKA: Health care provider, HCP)
– A trained person or an organisation that delivers proper health care (preventive, curative or rehabilitative) in a professional and systematic way to individual that needs health care services.
Heart attack:
– Occus when the flow of oxygen-carrying blood to the heart is blocked often due to fat build-up, cholesterol or other substances. For heart attack emergencies, AED units are helpful and may just save lives.
Hemorrhage:
– Another term for bleeding. A forceful escape of blood from a ruptured blood vessel, especially when there’s excessive discharge. Hemorrhage may be external (visible outside) and internal (no sign of bleeding outside the body).
Hyperglycaemia:
– The medical term for ‘high blood sugar’, often associated with diabetes (diabetes mellitus). When there is an excess blood sugar (glucose) in the blood and the body fails to convert it into energy.
Hypoglycaemia:
– The medical term for ‘low blood sugar’. The most common cause is when a person is taking Hyperglycaemia (diabetes mellitus) medications to lower down the blood sugar level.
Ibuprofen:
– A pain killer. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that relieves pain, reduces fever and inflammation by reducing hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body.
Incision:
– A surgical wound, clean-cut caused by a sharp-edged object usually, made with a knife.
Injury:
– A term that refers to harm or damage to the body due to accidents, falls, hits or weapons.
Insulin:
– A hormone secreted by the pancreas that converts blood sugar (glucose) from the food you eat into energy that the body can use to do work. Insulin regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. When control of insulin level fails, it can result in diabetes. Insulin may also refer to the synthesized insulin shots that are used to control blood sugar levels in diabetic persons.
Laboratory:
– A place where tests and research procedures are usually done to get more information of the patients health relating to identifying the nature of illness. Also known as Lab.
Laceration:
– A medical term for deep cut or tears in the flesh or skin.
Laxative:
– Used to prevent and treat constipation. It loosens the stools and increase bowel movement.
Lightheadedness:
– A common unpleasant sensation of dizziness and/or having a ‘going to faint’ feeling. It is mostly a symptom or result of an underlying condition.
Mini stroke:
– Also referred to as a transient ischaemic attack. This happens when a blood clot blocks the flow of blood in the brain.
Nausea:
– Also referred as motion sickness. It is a sensation of unease and discomfort and a feeling to vomit. It may have possible underlying causes.
Oedema:
– A condition distinguished as swelling which is caused when excess fluid leaks out of the body and build up. Swelling can usually be seen in the lower legs and ankles. Also spelled Edema.
Ointment:
– A topical medication applied to treat ailments by rubbing or applying to the skin. Ointments are for external use only.
Overdose:
– Taking an excessive dose of drugs, whether prescribed by the doctor, legal or illegal and over the counter drugs, which leads to a serious health condition, or worse, death. Check Alsco’sFirst Aid for Overdose to learn how to take care of yourself in case you get the symptoms.
Paracetamol:
– An effective over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. Also known as acetaminophen or APAP.
Paediatric:
– Branch of medicine that deals with the health and medical care of children from birth to 18 years old.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
– The equipment that is worn to minimize exposure to hazards. It can be clothing, goggles, helmet or anything that protects the body from hazard at work and minimises risk to health and safety.
Pharmacy:
– Science and technique of preparing and dispensing drugs. It is also where prescription medication and drugs are sold to the public.
Poison:
– Any substance or toxin that is harmful to the body. It can be in chemical form or gas form. Severe cases of poisoning can be life-threatening, First aid for poisoning can be performed to prevent/lessen the harm.
Prescription:
– A recommendation or instruction of treatment/medicine given by a doctor or medical practitioner to treat sickness or injury.
Primary Care:
– Day-to-day health care provided to patients by nurses or health care providers.
Primary Survey:
– A quick initial assessment of a patient’s health, injuries or conditions.
Pulse:
– Tactile arterial palpitation of the heartbeat. It can be palpated in any part of the body where an artery can be compressed against a bone. It is usually measured on the wrist or neck. Pulse is also equivalent to the heart rate.
Puncture:
– A wound or injury that has a small entry, which is in contrast to an open cut. This is caused by a pointed object such as nail that you accidentally stepped on which penetrated the skin. This wound carries danger of tetanus.
Recovery Position:
– Part of first aid treatment where an unconscious, yet breathing person is placed in a position that will ensure clear and open airways and make sure that possible vomit or fluid will not cause them to choke. For first aid training, refer to Managed Training Services.
Salbutamol:
– A medicine that used to relieve bronchospasm. It is used to relieve asthma and COPD.
Scoop Stretcher:
– Also known as a first aid device that is used to move injured people. It reduces possible undesirable movement of the injured person. It can also be used to transport patients.
Secondary Survey:
– An assessment of a patient with a more detailed content that involves patient observation and checking for injuries.
Seizure:
– A seizure occurs when there is an abnormal or uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain. It is used interchangeably with ‘convulsion’. Seizures usually happens to people with epileptic conditions.
Semi-prone position:
– A position of a patient lying on one side with one or both thighs or knees flexed on abdomen and arm on the lower side is extended.
Shock:
– A condition where in the body is not getting enough blood flow which can be life-threatening as the body will not be able to function properly due to lack of oxygen and nutrients supplied to the body. First aid for shock.
Sore:
– A term that refers to something painful or aching.
Sprain:
– An injury to the tissues surrounding a joint where ligaments are either stretched or torn that causes pain and swelling but not dislocated. Ankle sprain is the most common.
Stroke:
– Medical emergency when there is not enough oxygen or nutrients in a person’s brain because of a blood clot or bleeding in the brain.
Tetanus:
– A bacterial disease that is characterized by spasm of voluntary muscles usually brought through a wound or puncture by a contaminated object, such as rusty nails. Clostridium Tetani is the bacterium that caused an infection that generally enters through the skin.
Thermometer:
– A device that is used to measure temperature.
Topical:
– A medication that is applied to the skin or surface area to cure ailments. E.g. lotions, foams, gels, creams and ointments.
Trauma:
– Can be a physical or emotional injury resulting from a terrible event or accident.
Unconscious:
– The part of the mind that is not aware of the surroundings and oneself. This is due to lack of oxygen, shock, or injury.
Vertigo:
– The feeling where you sense that your environment is moving or spinning. It is a form of dizziness including a sensation of disorientation. This is usually which may go along with nausea, vomiting, or sweating. Don’t confuse vertigo with lightheadedness or dizziness. Know the Self-Help First Aid for Vertigo and its symptoms. If symptoms don’t go away, seek further medical advise.
Vomit:
– Is an act of involuntary ejection of contents of the stomach back into the mouth and outside the body. Other terms for vomit are emesis or throwing up.
Wound:
– An injury to living tissues usually characterized as skin cut or broken, typically open or closed.
X-ray:
– High-energy radiation in the form of electromagnetic. X-ray is used to make images of the internal part of the body like lungs that help to diagnose diseases and treat cancer.
First Aid Supplies Terms
ALSCO First Aid Booklet

If you need vital information about first aid treatments and procedures, you can always count on the ALSCO first-aid booklet. It includes step-by-step instructions to help you administer treatment.
Amputated Parts Bags

Amputated Parts Bags are used to preserve and protect amputated part of a patient or victim as a result of a traumatic injury. So it can be potentially used for replantation.
Antiseptic Cream

Antiseptic cream sachets are designed for one time use. This is easy to open and very handy. It is used to treat minor wounds and minimize the risk of infection.
Antiseptic Spray

Antiseptic spray is a multipurpose antiseptic to kill germs and sooth the affected area. This can be used for minor burns or sunburn, cuts, stings, insect bites, abrasions, itches.
Burn Dressing

Burn Dressing is used to cool and moisten burn injuries. It’s steeped in sterile burn gel. It helps the healing process while at the same time help protect the burn from infection.
Burn Gel

Burn gel gives relief to burns. It has a cooling and soothing element that helps the healing process while protecting the burns agains infections.
Butterfly Closures
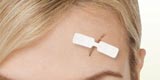
Butterfly closures are easy to use narrow sterile adhesive strips that are used to close open wounds. It holds the wound edges to stabilise the open wound without the help of stitches. Using butterfly closures will prevent scars due to sutures or staples.
Calico Triangular Bandages

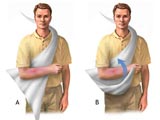
Calico Triangular Bandages are used to make slings and support the arm, protect injuries or elevate the limbs when necessary. You can adjust the length to make sure it fits comfortably and does not stress the injured body part.
Cleansing Wipes

Cleansing Wipes are antiseptic wipes used to clean wounds after washing them with water. They sterilise small wounds and kills the germs to avoid infection.
Combine Dressing

Combine Dressing are special square dressings that are highly absorbent. They are suited for wounds that are heavily bleeding.
Conforming Bandage


Confirming Bandages are used to provide compression and support. They are pliable and lightweight. This is great at securing dressings, small limbs and wounds and those difficult-to-dress wounds. They are flexible and come in different sizes.
Contaminated Waste Bag

Contaminated waste bags are used to dispose contaminated wastes. They are heavy duty and have Hi-Visibility for easy identification and to make sure that they are disposed properly.
Cotton Tip Applicators Sterile

Cotton tip applicators are used for wound cleaning or applying medicinal gel/cream to the affected areas. Cotton tip applicators can be sterile or non sterile.
CPR Face Mask in Bag

CPR Face Mask is used as a personal protection when you perform a resuscitation on an injured patient and to provide airway management as well as assist in the safe application of CPR.
Elastic Crepe Band

An Elastic Crepe Band is a stretchable bandage that is used to treat muscle strains and sprains and fractures. It creates a localised pressure. It reduces the flow of blood to a particular area by applying even and stable pressure.
Eye Pads

Eye Pads are small pads that are used to protect minor eye injuries. It is used with a bandage to shield eyelid cuts and to protect it from small foreign, non-embedded objects.
Eye Spears

Eye Spears are sponges that are highly absorbent used to clean eye injuries. These are helpful in freeing dirt and other small, foreign and non-embedded objects from the eyes. These can also be used to dab away the blood and washing solutions.
Eye Wash Liquid Ampoule

An Eye Wash liquid ampoule is made of Sodium Chloride solution (0.9%) used as a handy, easy-to-use sterile eye wash. Simply twist off the top to open. These sealed capsule-like ampoules are good for single-use only.
Fabric Dressing Strip

Fabric Dressing Strips are used to cover and protect small cuts and burns. They are flexible and breathable. These are conforming and have excellent adhesion features.
Fabric F/Tip & Knuckle
The Fabric Knuckle paster is especially designed to to cover and protect minor cuts and burns on the knuckle area.
Face Shield Disposable

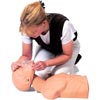
Disposable Face Shield is used to protect the person when performing a resuscitation. This is an essential instrument when performing a CPR to individuals suffering from either a cardiac or pulmonary arrest. It provides a barrier or shield from possible infections through body fluids.
Finger Dressing

Finger Dressings are dressings are general purpose wound dressing that can treat finger cuts or wounds that are too large to cover with an adhesive dressing.They are made of highly absorbent wound pads that can absorb wound exudates and stops bleeding. It is available in different sizes.
Forceps Stainless Steel

Stainless steel forceps are essential for removing non-embedded foreign objects from wounds in emergency situations.
Gauze Swab

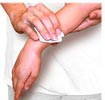
Gauze Swabs are absorbent materials that are used to clean wounds and manage blood flow. They are also used as padding to keep the wounds dry, perfectly sized to swab away the dirt and blood from the wound.
Instant Ice Pack

Instant Ice Packs are used as first aid on injuries or cuts. They can instantly produce cold to relieve inflammation and pain due to injury. Instand Ice Packs are a convenient replacement for crushed ice when it is not available.
Kidney Dish Plastic

Kidney dishes are used in medical and surgical wards to receive medical wastes and soiled dressings. It’s kidney shaped design allows it to be held against the patients body so it can easily catch debris or falling fluids.
Low Adherent Dressing

Low Adherent Dressings are absorbent dressings that come in different sizes. They are used to absorb exudate or fluid from wounds, it also acts a protective pad and a physical barrier to infection.
Micro Paper Tape

Microporous Paper Tape is a thin tape used for fragile, sensitive skin. It’s breathable, hypoallergenic and water-permeable. It’s used to secure dressings to sensitive wounds or facial injuries.
Needle Disposal Unit

Needle Disposal Unit is a bin used to dispose sharp wastes like syringes, needles, razor blades, or broken glass.
Nitrile Gloves With Powder Free

Nitrile Gloves are disposable medical gloves that are made with nitrile rubber . They are latex-free perfect for individuals with latex allergies and powder-free to prevent possible powder-related complications. They are worn when administering first-aid to injured person, cleaning or treating wounds.
Plastic Plaster Strips
Plastic Plaster Strips are used to cover and protect all types of small wounds from exposure to dirt or dust. They’re made from breathable and water-repellent materials. They are important basic first-aid for small and minor grazes, burns, and cuts.
Safety Pins

Safety Pins are also first-aid kit essentials. They are used to secure dressings, slings and bandages. They come in different sizes for various affixing needs.
Scissors Sharp/Blunt

Stainless steel scissors are versatile first-aid items. They can be used for cutting clothing to expose wounded areas for treatment. They are also used to cut bandages and tape to correct sizes.
Small Pencil Torch

Pencil torches are used when doing medical procedures or when examining injured or infected parts that needs lighting like inside the mouth, ears, nose or eyes.
Splinter Probe Disposable


The disposable splinter probe is used to locate and remove splinters. Individually packed, these splinter probes are hygienic and easy to use. They are designed to remove particles painlessly and safely.
Thermal Blanket


Thermal Blanket is an emergency blanket that provides warmth by retaining body heat. This thermal blanket can be used to as a shelter, windproof and waterproof barrier, and protection for anyone suffering from hypothermia or shock.
Wound Dressing


The Wound Dressing is a handy combination of flexible gauze bandage and sterile, non-absorbent pad. It is suited for large, serious cuts and burns. This can also be used for managing bleeding and protecting large wounds.
Zinc Oxide Tape

Zinc Oxide Tape is a versatile first-aid tape. Zinc oxide tape can be used for protecting skin from blisters, supporting small sprains in the fingers or toes, and affixing pads or dressings. Zinc oxide tape is recommended for use only on non-sensitive skin, not including facial or burned skin.
Alsco’s cost-effective renting solution gives you a variety of hassle-free First Aid Kit services. Want to make sure you keep up with WH&S compliance? Partner with Alsco! Call 1300 077 391 now.


